Log Collection¶
When a user wants to download logs from the Edge Device UI (how to download logs), Device Builders must ensure that logs are collected and placed in a specified folder.
Responsibilities of IEDK GetLogFile rpc Method¶
- Collect journalctl outputs
- If additional log files exist that do not use journalctl, these log files can be added (optional)
- Compress the log files and place the archived file to the requested directory
- Return the full path of the log file
Log Collection Scenario¶
The Edge Device UI should call the GetLogFile method with an existing directory name as a request parameter, the GetLogFile rpc method must handle the log collection, compression, naming etc.
You can get whole system logs from journalctl with the following command:
journalctl > logs
Or just add specific logs:
journalctl -u networking > logs
If you want, you can add custom logs as well.
Let's assume that you have a log file named myCustomLogFile.
cat myCustomLogFile >> logs
You need to compress the collected log file and put it under the requested directory.
NOTICE
If the requested directory does not exist, the service need to return an error because the creation of the directory is not the responsiblity of GetLogFile rpc method.
tar -czvf /requested_path/devicelogs_devicename_timestamp.tar.gz logs
GetLogFile rpc method must return the full log file path as response. For the case above, /requested_path/devicelogs_devicename_timestamp.tar.gz should be returned.
Log File Naming¶
There are no restrictions on the naming of the collected logs. It is recommended to use a unique identifier in the log name that describes the device individually, for example: devicelogs_devicename_timestamp.tar.gz
Custom Log Collection and Forwarding to Third-party IT Infrastructure¶
Device Builders can set up the log collector by modifying the host.log.driver capability in the capabilities.json. This configuration allows users to efficiently route collected logs to their specified IT infrastructure. Available collector options include:
- syslog: Create a
/var/run/syslog.socksocket file in edge iot core to accept log data. - systemd: Reads log data from the
/host-system/var/log/journalfolder, and it serves as the default log collector. - tail: Reads log data from the
/data/agent/tail-logfile. - none: No logs will be collected and forwarded.
Capability Example¶
Below is a simplified capabilities.json configuration example, setting only the host.log.driver capability:
{
"capabilityId": "host.log.driver",
"name": "Select log driver for device",
"description": "Only one driver can be selected, systemd is the default selection.",
"scope": "protected",
"property": "optional",
"details": {
"exLogDriver": "systemd"
}
}
Deploying via docker compose¶
It is important to mount files or directories to different log collectors. Below is a simplified docker-compose.yml example that shows setups for different types of log collectors:
version: "2.4"
services:
industrial-edge:
restart: always
environment:
- HostIps=X.X.X.X
volumes:
- "/etc/capabilities.json:/data/app_engine/Configuration/capabilities.json"
- "/host-system/xxx/journal:/host-system/var/log/journal" # systemd collector
- "/host-system/xxx:/var/run" # syslog collector
- "/host-system/xxx/tail-log:/data/agent/tail-log" # tail collector
ports:
- "443:443"
container_name: edge-iot-core
image: edge_iot_core:1.16.0
Forwarding to Third-party IT Infrastructure¶
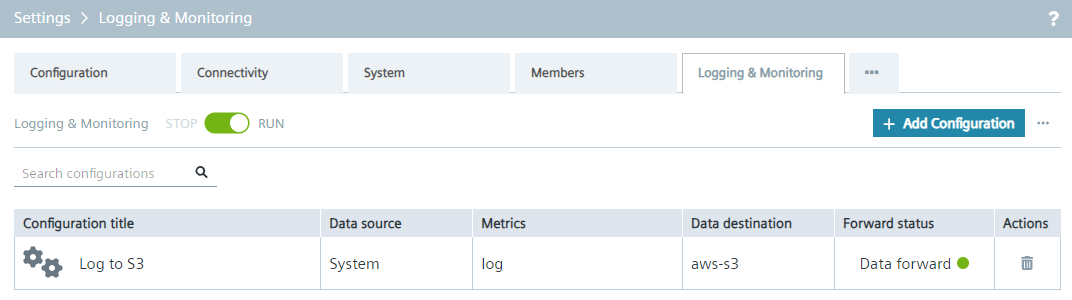
Logs can be forwarded to third-party IT infrastructures via Logging & Monitoring. For example, to forward system logs to AWS S3:
- Log in to the IED UI, navigate to
Settings > Logging & Monitoring, and Creating Configuration to forward the system log to AWS S3.
2.After configuration, access your AWS S3 service to verify that the system log was successfully forwarded to the specified bucket.